Table of Contents
Construction of Cycloidal Curves – Cycloid, Epicycloid and Hypocycloid/साइक्लोइडल कर्व्स का निर्माण – साइक्लोइड, एपिसाइक्लॉइड और हाइपोसाइक्लॉइड
These curves are generated by a fixed point on the circumference of a circle, which rolls without slipping along a fixed straight line or a circle. The rolling circle is called generating circle and the fixed straight line or circle is termed directing line or directing circle. Cycloidal curves are used in tooth profile of gears of a dial gauge.
ये वक्र एक वृत्त की परिधि पर एक निश्चित बिंदु द्वारा उत्पन्न होते हैं, जो एक निश्चित सीधी रेखा या एक वृत्त के साथ फिसले बिना लुढ़कता है। रोलिंग सर्कल को जनरेटिंग सर्कल कहा जाता है और निश्चित सीधी रेखा या सर्कल को डायरेक्टिंग लाइन या डायरेक्टिंग सर्कल कहा जाता है। डायल गेज के गियर्स के टूथ प्रोफाइल में साइक्लोइडल कर्व्स का उपयोग किया जाता है।
Construction of Cycloid/चक्रज का निर्माण-
Cycloid is a curve generated by a point on the circumference of a circle which rolls along a straight line. It can be described by an equation, y = a (1 – cosθ) or x = a (θ – sinθ).
साइक्लोइड एक वक्र है जो एक वृत्त की परिधि पर एक बिंदु द्वारा उत्पन्न होता है जो एक सीधी रेखा के साथ घूमता है। इसे एक समीकरण,y = a (1 – cosθ) or x = a (θ – sinθ) द्वारा वर्णित किया जा सकता है।
Construct a cycloid, when the generating circle diameter is given./एक चक्रज का निर्माण करें, जब जनक वृत्त व्यास दिया गया हो।
(i) With centre C and given radius R, draw a circle. Let P be the generating point.
(ii) Draw a line PA tangential to and equal to the circumference of the circle.
(iii) Divide the circle and the line PA into the same number of equal parts, say 12, and mark the division-points as shown.
(iv) Through C, draw a line CB parallel and equal to PA.
(v) Draw perpendiculars at points 1, 2 etc. cutting CB at points C1, C2 etc.
Assume that the circle starts rolling to the right. When point 1′ coincides with 1, centre C will move to C1• In this position of the circle, the generating point P will have moved to position P1 on the circle, at a distance equal to P’1 from point 1. It is evident that P1 lies on the horizontal line through 1′ and at a distance R from C1 . Similarly, P2 will lie on the horizontal line through 2′ and at the distance R from C2.
(vi) Through the points 1 ‘, 2’ etc. draw lines parallel to PA.
(vii) With centres C1, C2 etc. and radius equal to R, radius of generating circle, draw arcs cutting the lines through 1 ‘, 2’ etc. at points P1, P2 etc. respectively. Draw a smooth curve through points P, P1, P2 •••• A. This curve is the required cycloid.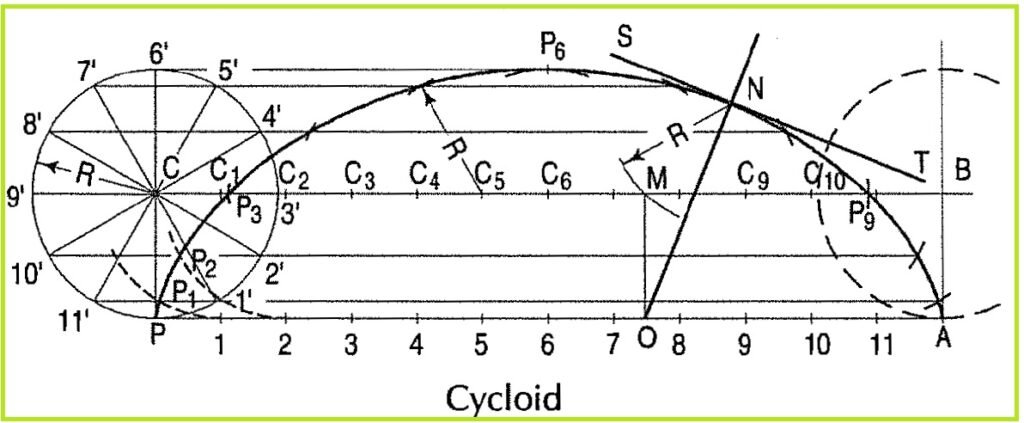
(i) केंद्र C और त्रिज्या R लेकर एक वृत्त खींचिए। P को जनरेटिंग पॉइंट होने दें। (ii) वृत्त की परिधि को स्पर्श करने वाली और उसके बराबर एक रेखा PA खींचिए।
(iii) वृत्त और रेखा PA को समान भागों में विभाजित करें, मान लीजिए 12, और दिखाए गए अनुसार विभाजन-बिंदुओं को चिह्नित करें।
(iv) C से होकर PA के समानान्तर और बराबर एक रेखा CB खींचिए।
(v) बिंदु 1, 2 आदि पर लंब खींचिए, CB को बिंदु C1, C2 आदि पर काटिए।
मान लें कि वृत्त दाईं ओर लुढ़कना शुरू करता है। जब बिंदु 1′ 1 के साथ मेल खाता है, तो केंद्र C, C1 पर चला जाएगा • सर्कल की इस स्थिति में, जनरेटिंग पॉइंट P, बिंदु 1 से P’1 के बराबर दूरी पर सर्कल पर P1 की स्थिति में चला गया होगा। यह है स्पष्ट है कि P1 क्षैतिज रेखा पर 1′ के माध्यम से और C1 से R की दूरी पर स्थित है। इसी प्रकार, P2 क्षैतिज रेखा पर 2′ के माध्यम से और C2 से R की दूरी पर स्थित होगा।
(vi) बिंदुओं 1′, 2′ आदि से PA के समांतर रेखाएँ खींचिए।
(vii) C1, C2 आदि केंद्रों और R के बराबर त्रिज्या के साथ, उत्पन्न वृत्त की त्रिज्या, क्रमशः P1, P2 आदि बिंदुओं पर 1′, 2′ आदि के माध्यम से रेखाओं को काटते हुए चाप खींचें। बिंदु P, P1, P2 •••• A के माध्यम से एक चिकनी वक्र बनाएं। यह वक्र आवश्यक साइक्लोइड है।
Normal and tangent to a cycloid:/ चक्रज के लिए सामान्य और स्पर्शरेखा: सभी चक्रज वक्र के लिए एक सामान्य बनाने का नियम :
The rule for drawing a normal to all cycloidal curves:
The normal at any point on a cycloidal curve will pass through the corresponding point of contact between the generating circle and the directing line or circle.
The tangent at any point is perpendicular to the normal at that point.
साइक्लॉयडल वक्र पर किसी भी बिंदु पर सामान्य जनरेटिंग सर्कल और डायरेक्टिंग लाइन या सर्कल के बीच संपर्क के संबंधित बिंदु से होकर गुजरेगा।
किसी भी बिंदु पर स्पर्शरेखा उस बिंदु पर सामान्य के लंबवत होती है।
To draw a normal and a tangent to a cycloid at a given point N on it./किसी चक्रज के दिए गए बिंदु N पर उस पर एक सामान्य और एक स्पर्शरेखा खींचना।
(i) With centre N and radius equal to R, draw an arc cutting CB at M.
(ii) Through M, draw a line MO perpendicular to the directing line PA and cutting it at O. O is the point of contact and M is the position of the centre of the generating circle, when the generating point P is at N.
(iii) Draw a line through N and O. This line is the required normal.
(iv) Through N, draw a line ST at right angles to NO. ST is the tangent to the cycloid.
(i) N को केंद्र और R को त्रिज्या लेकर एक चाप लगाइए जो CB को M पर काटता है।
(ii) एम के माध्यम से, एक रेखा एमओ को डायरेक्टिंग लाइन पीए के लंबवत खींचें और इसे ओ पर काट दें। ओ संपर्क बिंदु है और एम जनरेटिंग सर्कल के केंद्र की स्थिति है, जब उत्पादन बिंदु पी एन पर है।
(iii) एन और ओ के माध्यम से एक रेखा खींचें। यह रेखा आवश्यक सामान्य है।
(iv) N से होकर NO के समकोण पर एक रेखा ST खींचिए। ST चक्रज की स्पर्शरेखा है।
Epicycloid and Hypocycloid/एपिसाइक्लॉइड और हाइपोसाइक्लॉइड
The curve generated by a point on the circumference of a circle, which rolls without slipping along another circle outside it, is called an epicycloid.
When the circle rolls along another circle inside it, the curve is called a hypocycloid.
एक वृत्त की परिधि पर एक बिंदु द्वारा उत्पन्न वक्र, जो इसके बाहर किसी अन्य वृत्त के साथ फिसले बिना लुढ़कता है, एक एपिसाइक्लॉइड कहलाता है।
जब वृत्त अपने भीतर किसी अन्य वृत्त के साथ घूमता है, तो वक्र को हाइपोसाइक्लॉइड कहा जाता है।
Draw an epicycloid and a hypocycloid when the generating circle radius r & directing circle radius R are given./जब वृत्त त्रिज्या आर और निर्देशन वृत्त त्रिज्या आर दिए गए हों तो एक एपिसाइक्लॉइड और एक हाइपोसाइक्लॉइड बनाएं।
Epicycloid : With centre O and radius R, draw the directing circle (only a part of it may be drawn). Draw a radius OP and produce it to C, so that CP = r.
With C as centre, draw the generating circle. Let P be the generating point. In one revolution of the generating circle, the point P will move to a point A, so that the arc PA is equal to the circumference of the generating circle. The position of A may be located by calculating the angle subtended by the arc PA at centre O, by the formula,
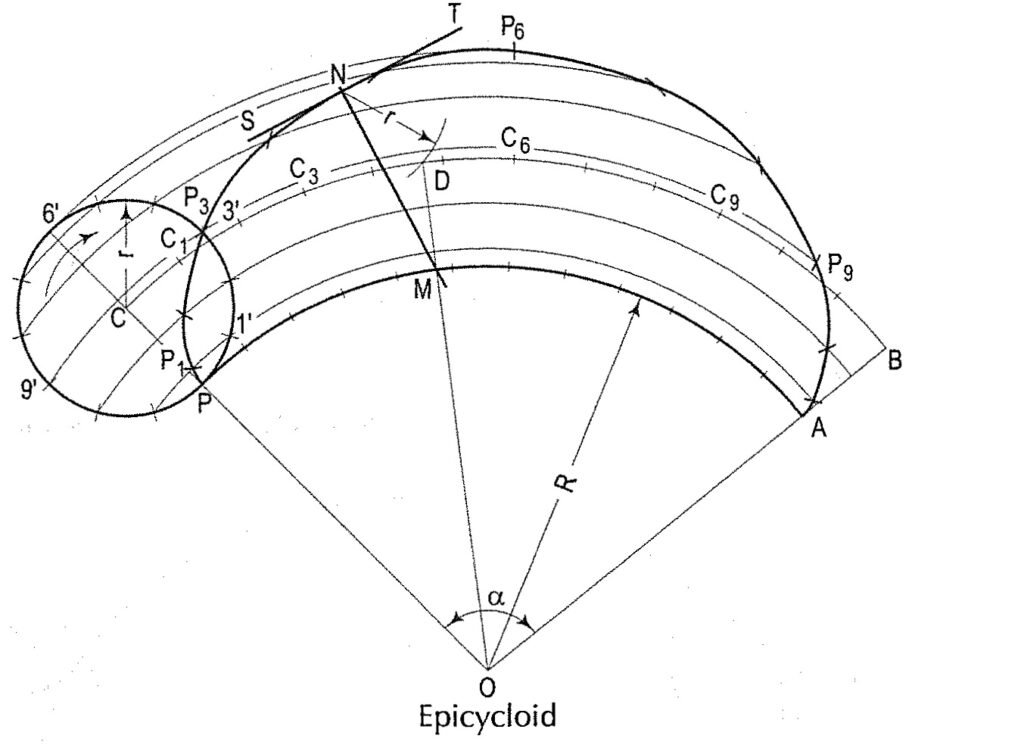 (i) Set-off this angle and obtain the position of A.
(i) Set-off this angle and obtain the position of A.
(ii) With centre O and radius equal to OC, draw an arc intersecting QA-produced at B. This arc CB is the locus of the centre C.
(iii) Divide CB and the generating circle into twelve equal parts.
(iv) With centre 0, describe arcs through points 1′, 2′, 3′ etc.
(v) With centres C1, C2 etc. and radius equal to r, draw arcs cutting the arcs through 1 ‘, 2’ etc. at points P1, P2 etc. Draw the required epicycloid through the points P, P1, P2 •..••• .A.
एपिसाइक्लॉइड: केंद्र ओ और त्रिज्या आर के साथ, निर्देशित सर्कल (केवल
इसका एक हिस्सा खींचा जा सकता है)। एक त्रिज्या OP खींचिए और इसे C तक बढ़ाइए, ताकि CP = r हो।
C को केंद्र मानकर, जनरेटिंग सर्कल बनाएं। P को जनरेटिंग पॉइंट होने दें। जनरेटिंग सर्कल की एक क्रांति में, बिंदु P बिंदु A पर चला जाएगा, ताकि आर्क PA, जनरेटिंग सर्कल की परिधि के बराबर हो।
चाप PA द्वारा केंद्र O पर अंतरित कोण की गणना सूत्र द्वारा A की स्थिति का पता लगाया जा सकता है,
(i) इस कोण को सेट-ऑफ करें और A की स्थिति प्राप्त करें।
(ii) केंद्र O और OC के बराबर त्रिज्या के साथ, B पर बने QA को काटता हुआ एक चाप बनाएं। यह चाप CB केंद्र C का बिंदुपथ है।
(iii) CB और जनरेटिंग सर्कल को बारह बराबर भागों में विभाजित करें।
(iv) केंद्र 0 के साथ, बिंदु 1′, 2′, 3′ आदि के माध्यम से चापों का वर्णन करें।
(v) केंद्र C1, C2 आदि और r के बराबर त्रिज्या के साथ, 1′, 2′ आदि बिंदुओं को P1, P2 आदि पर काटते हुए चाप बनाएं। बिंदुओं P, P1, P2 • के माध्यम से आवश्यक एपिसाइक्लॉइड बनाएं।
Hypocycloid: The method for drawing the hypocycloid is same as for epicycloid. Note that the centre C of the generating circle is inside the directing circle.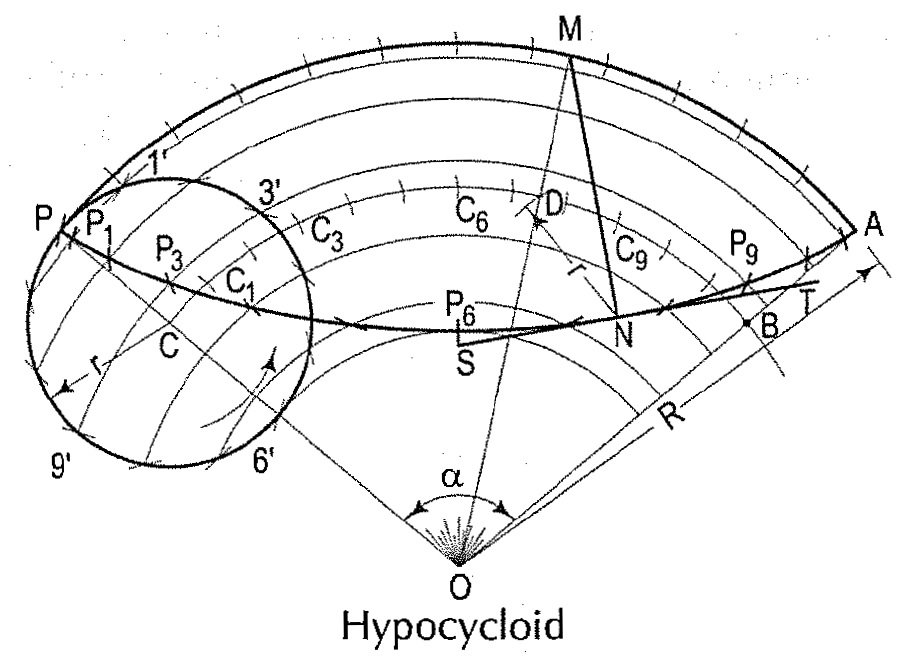
हाइपोसाइक्लॉइड: हाइपोसाइक्लॉइड को खींचने की विधि एपिसाइक्लोइड के समान है। ध्यान दें कि जनरेटिंग सर्कल का केंद्र C डायरेक्टिंग सर्कल के अंदर है।
Normal and tangent to an epicycloid and a hypocycloid:/एक एपिसाइक्लॉइड और हाइपोसाइक्लॉइड के लिए सामान्य और स्पर्शरेखा:
To draw a normal and a tangent to an epicycloid and a hypocycloid at a point N./एक बिंदु N पर एक एपिसाइक्लॉइड और एक हाइपोसाइक्लॉइड के लिए एक सामान्य और एक स्पर्शरेखा खींचना।
(i) With centre N and radius equal tor, draw an arc cutting the locus of the centre C at a point D.
(ii) Draw a line through O and D, cutting the directing circle at M.
(iii) Draw a line through N and M. This line is the normal. Draw a line ST through N and at right angles to NM. ST is the tangent.
(i) केंद्र N और बराबर त्रिज्या लेकर एक चाप खींचिए जो बिंदु C को बिंदु D पर काटता है।
(ii) दिशा वृत्त को M पर काटते हुए O और D से होकर एक रेखा खींचिए।
(iii) N और M से होकर एक रेखा खींचिए। यह रेखा अभिलंब है। N से होकर NM के समकोण पर एक रेखा ST खींचिए। एसटी स्पर्शरेखा है।

